South Asia has last hosted a WCEE in 1977 when India hosted the 6WCEE at New Delhi. South Asia covers 3.5% of the world's land surface area, but has a population of more than 2 billion or about 25% (one-fourth) of the world's population, making it both the most populous and the most densely populated geographical region in the world. Also, South Asia is home to many highly seismically vulnerable nations on the planet. Hosting 18WCEE in India will go a long way in sustaining the discourse among the policymakers of the highly seismically vulnerable South Asian nations on the importance of funding Disaster Risk Research and thus will have a greater contribution towards global seismic risk reduction compared to hosting in other bidding nations.
India's Relevance to the 19WCEE
- India sits at the collision point of the Indo-Australian and Eurasian plates, making it one of the most seismically active regions.
- Over 15% of the world's great earthquakes (M8.0) in 20th century occurred in India.
- More than half of India's land area is vulnerable to earthquakes.
- The country has a history of devastating earthquakes, with a major one expected in the Himalayas.
- The Great Indian Earthquake, which occurred on January 15, 1934, was one of the most powerful earthquakes in recorded history. It had a magnitude of 8.1 and caused extensive damage in the Bihar-Nepal region, with an estimated death toll of over 10,000 people.
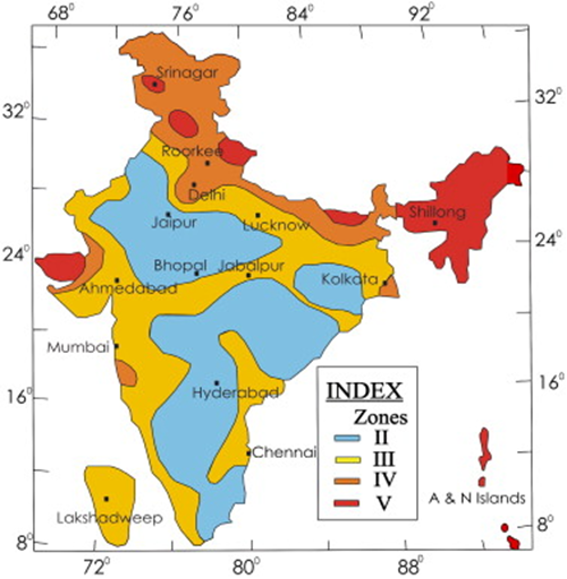
FORECAST OF FUTURE EARTHQUAKES IN SEISMIC GAPS OF HIMALAYAS (BILHAM ET AL., 2019)
Traditional Earthquake Resistant Building Systems
- Ancient Indian builders used innovative techniques like the Sandbox method, which involves using a cushion of sand to absorb earthquake vibrations.
- Temples and structures built using this technique have withstood earthquakes over centuries.
Dhajji Dewari Buildings, Kashmir
- Significance: Features a timber frame filled with unburnt clay bricks, providing flexibility and resistance to seismic forces.

Dhajji Dewari Buildings, Kashmir
Traditional House in Kutch Region
- Significance: Constructed using local materials like mud and thatch, showcasing earthquake-resistant techniques with low-cost materials.

Traditional House in Kutch Region
A Typical House in Assam
- Significance: Utilizes bamboo and thatch, showcasing a lightweight and flexible structure that can withstand seismic forces.

A Typical House in Assam
Koti Banal Architecture of Uttarakhand
- Significance: Characterized by stone masonry and wooden beams, demonstrating a robust construction method that adapts to seismic movements.

Koti Banal Architecture of Uttarakhand
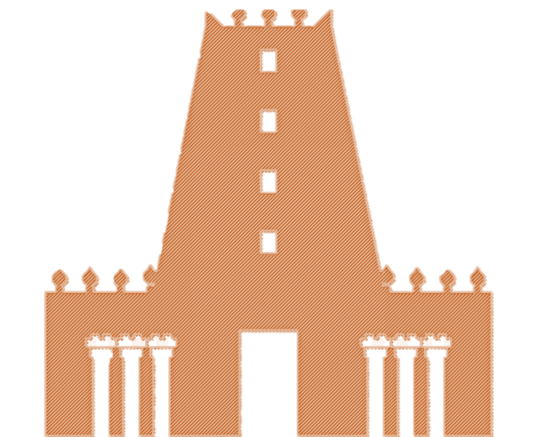
RAMAPPA TEMPLE
- Location: Palampet, Telangana, India
- Significance: Built in 1213 AD during the reign of the Kakatiya dynasty, the Ramappa Temple is renowned for its exquisite architecture and the use of the sandbox technique in its foundation.
- Sandbox Technique: The temple's foundation is said to be laid on a sandbox, which acted as a cushion to absorb seismic vibrations, ensuring the temple's stability during earthquakes.
- Architectural Marvel: The temple is a testament to the advanced engineering and architectural skills of ancient India, with intricate carvings and a unique floating brick technique used in its construction.
- Cultural Heritage: Recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage Site, the Ramappa Temple is a symbol of India's rich cultural and architectural heritage, attracting visitors from around the world.

RAMAPPA TEMPLE
THOUSAND PILLAR TEMPLE
- Location: Warangal, Telangana, India
- Significance: Built in 1163 AD by King Rudra Deva, the Thousand Pillar Temple is renowned for its unique architectural style and earthquake-resistant construction.
- Architecture: The temple is known for its intricate carvings, richly carved pillars, and a unique star-shaped platform. It is dedicated to Lord Shiva, Lord Vishnu, and Lord Surya.
- Earthquake Resistance: The temple is believed to have been constructed using a technique that made it earthquake-resistant, with the pillars not touching the ground directly but resting on a base plate.
- Cultural Heritage: The Thousand Pillar Temple is an important heritage site in India, reflecting the architectural and engineering brilliance of ancient times.

THOUSAND PILLAR TEMPLE
Current Scenario
- India's seismic activity is complex, with varying risk factors like population density and poor construction quality.
- Earthquake awareness is not yet a concern for general public. This conference aims to enhance the awareness and educate the public with current scenario.
- The Disaster Management Act of 2005 provides a framework for disaster response, including earthquakes. The Government of India enacted the Disaster Management Act, which envisaged the creation of the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) chaired by the Prime Minister of India.

Collapsed Bhuj Central Hospital (2001)
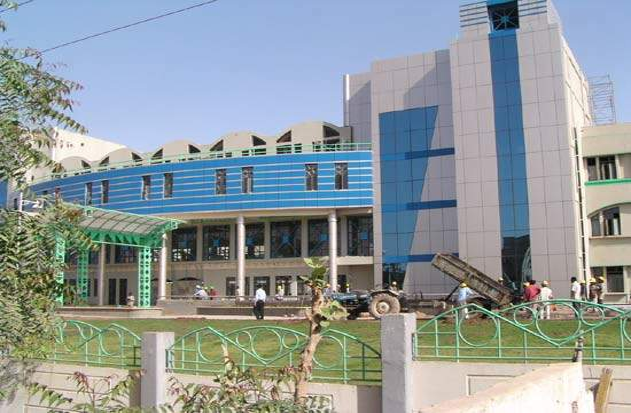

Earthquake Resistant Hospital in Bhuj
Hosting WCEE in India
- Raises awareness among policymakers, administrators, and the public about earthquake safety and mitigation.
- Helps disseminate knowledge on earthquake-resistant design, particularly its benefits for developing economies.
- India is not only a signatory to the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction but also proudly committed to its principles, aligning with nations worldwide in advancing disaster risk reduction and resilience.
Diverse Climatic Zones - Melting Pot of Diverse Cultures
- India's diverse climatic zones offer a range of adventure and nature events, enhancing the conference experience.

Gulmarg, Jammu and Kashmir

Velankanni Church, Nagapattinam

Golden Temple, Amritsar

Hawa Mahal, Jaipur

Taj Mahal, Agra

Ellora Caves, Aurangabad

Cavelossim Beach, Goa

Corbett Tiger Reserve, Uttarakhand
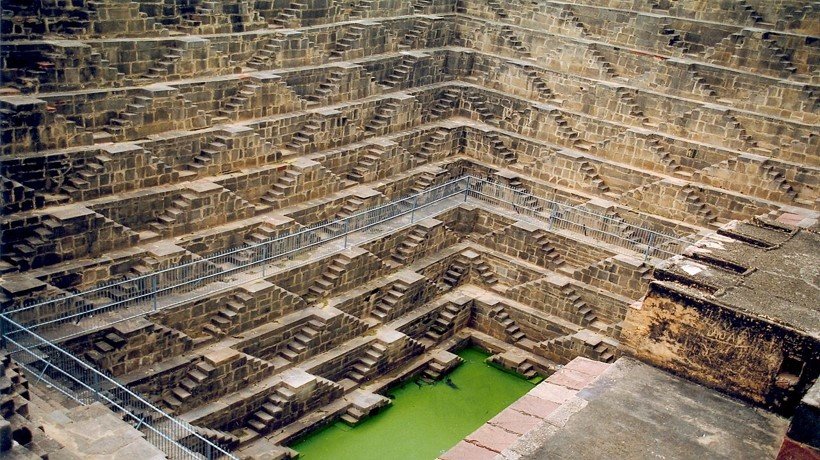

Stepped Well, Rajasthan
Flavors of India: Culinary Diversity and Spice Culture

CULINARY DIVERSITY

LAND OF SPICES
September's Embrace: The Perfect Season for 19WCEE
- Delightful Weather: Experience Delhi's pleasant weather with an average temperature of 25 °C.
- Cultural Extravaganza: Immerse yourself in the vibrant festivities of Onam, Navratri, Durga Puja, Dushera and Diwali.
- Artistic Marvels: Immerse yourself in a cultural tapestry woven with events like the vibrant Ladakh Festival, the enchanting Ram Leela, the mesmerizing Gavari - Sacred Dance Drama Festival, and a myriad of other famous folk festivals and art celebrations.
- Adventurous Escapades: Explore the beauty of nature with activities like Valley of Flowers trek, Camel Safari in Rajasthan, White Water River Rafting, Spiti Valley Trekking, Mysuru Dushera, Marwar Festival and Visits to Ram Mandir, Taj Mahal, Golden Temple, Tawang Moastery, Famous Churches in South.

Ganga aarti at Haridwar

Rajasthan International Folk Festival

Mysuru Dushera Festival

Largest monastery Tawang, A.P.

River Rafting Rishikesh

Marwar Festival Jodhpur
New Delhi: The Gateway to Seamless
Connectivity and Accessibility
- International Connectivity: Indira Gandhi International Airport (IGIA) in New Delhi connects to major cities in most of the countries worldwide, facilitating easy access for int. participants.
- Tourism Hub: Delhi's central location makes it a perfect hub for exploring nearby tourist destinations. For example, the iconic Taj Mahal is just a 3-hour drive from the conference venue via the Taj/Yamuna Expressway.
- Efficient Metro System: Delhi boasts an extensive metro network that links key landmarks and areas, providing convenient and affordable transportation options for attendees.
- Varied Transport Options: In addition to the metro, attendees can choose from prepaid taxis, app-based taxi aggregators, and buses to navigate the city, ensuring flexibility and ease of travel during the conference.
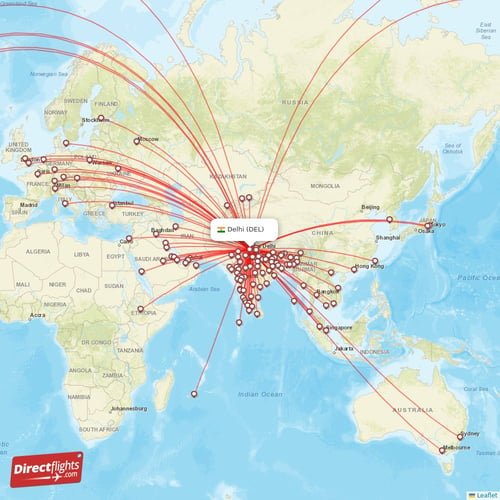
Non-stop International flights from New Delhi (DEL)

Non-stop domestic flights from New Delhi (DEL)
Hosting the WCEE in India not only benefits the country but also contributes to global efforts in earthquake preparedness and safety.